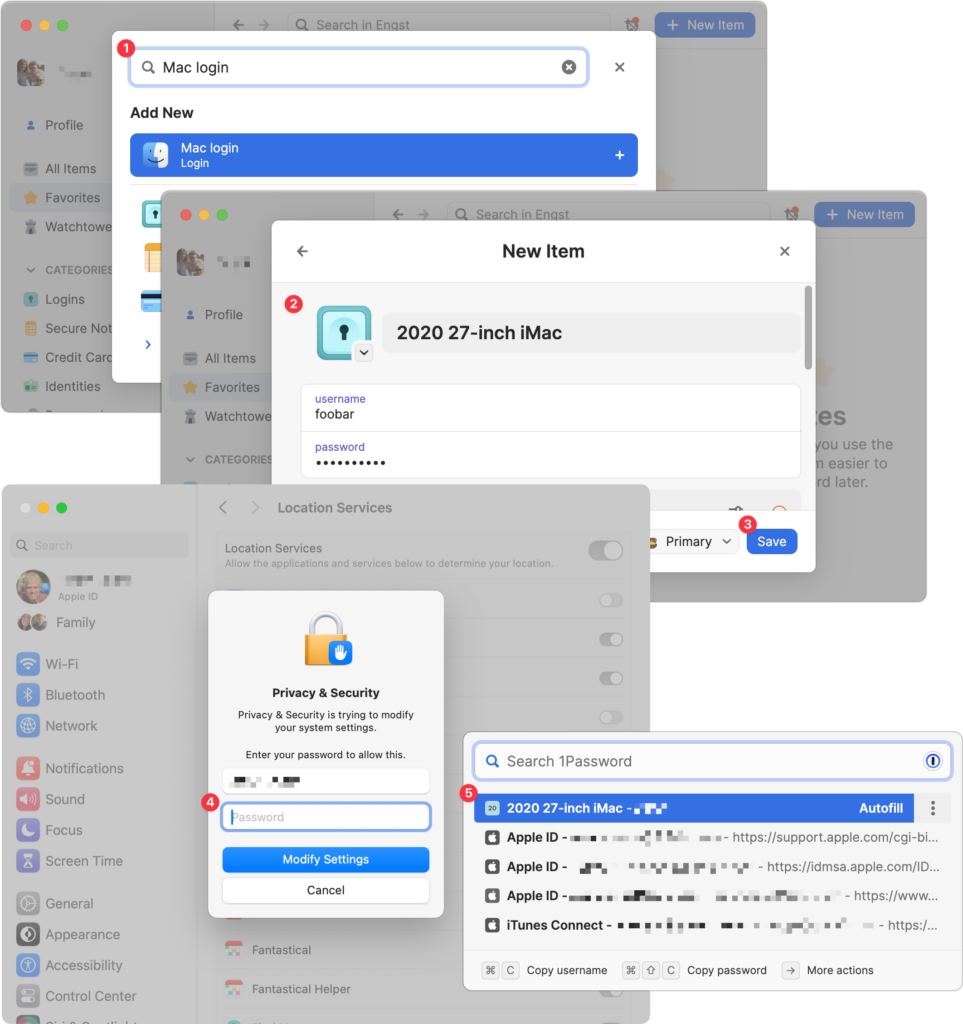
Use 1Password to Enter Your Mac Login Password
We think of 1Password as being helpful for entering passwords on websites and in iPhone and iPad apps. But its Universal Autofill feature has a hidden capability that lets 1Password enter your Mac login password when you have to provide it to change certain system settings, install apps, format drives in Disk Utility, and more. (But it won’t work to log in at startup before 1Password is running.) To turn this feature on, click the New Item button in 1Password, search for and select “Mac login” ➊, give it a name that will sort alphabetically to the top, like “2020 27-inch iMac” ➋, enter your password, and click Save ➌. From then on, whenever you’re prompted for your Mac login password ➍, press Command-\ (Backslash, located above the Return key), and then click the desired login or press Return to select the topmost item ➎.
(Featured image based on an original by iStock.com/ipuwadol)
Social Media: 1Password is tremendously helpful for entering website passwords, but a little-known feature also enables it to enter your Mac login password for changing system settings, installing apps, and more.











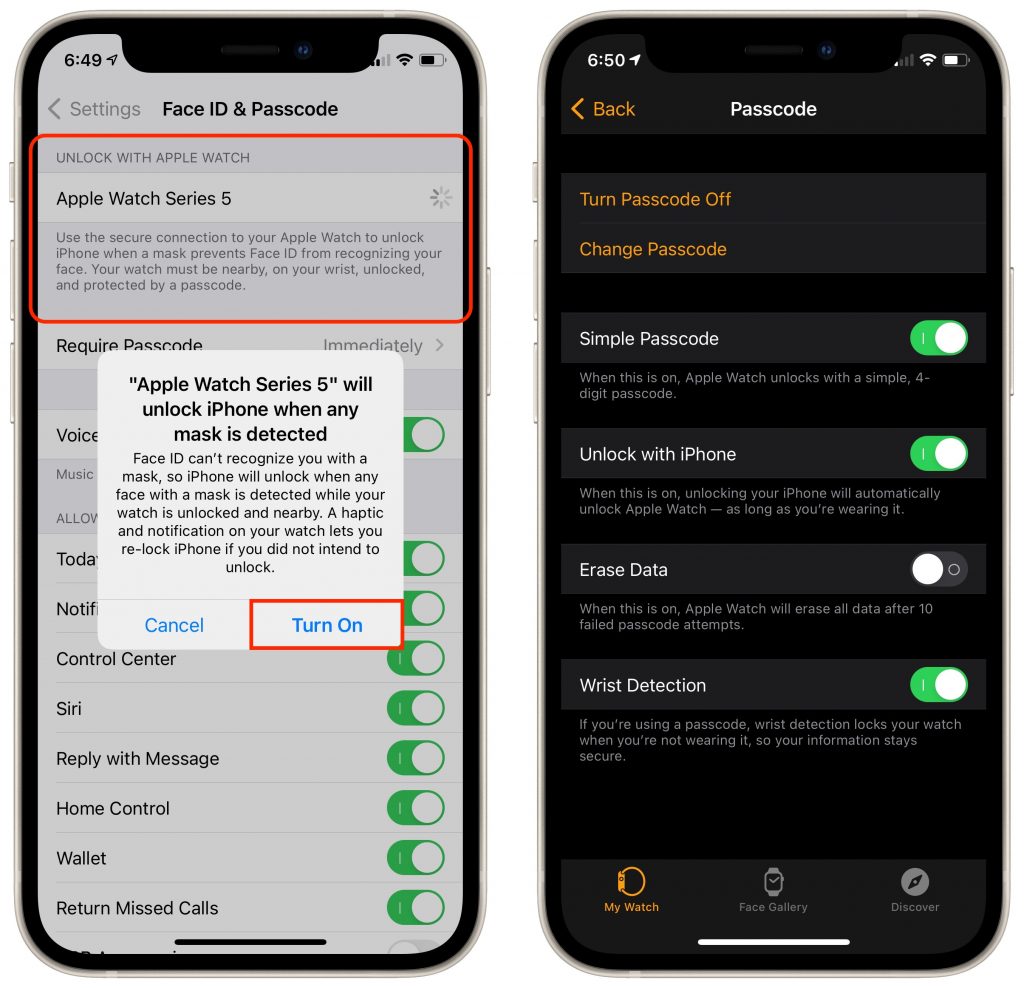
 Here’s how it works. Once you’ve updated your Face ID–enabled iPhone to iOS 14.5 and your Apple Watch Series 3 or later to watchOS 7.4, you can enable the Unlock with Apple Watch setting. From then on, if your mask prevents Face ID from unlocking your iPhone, iOS will check to see if your watch is nearby, on your wrist, protected by a passcode, and unlocked. If so, your iPhone unlocks immediately, just as though it had scanned your face successfully. Your Apple Watch also taps your wrist to alert you and give you the option of locking the iPhone again, just in case someone has surreptitiously snagged your iPhone and is using the feature to unlock it in your presence.
Here’s how it works. Once you’ve updated your Face ID–enabled iPhone to iOS 14.5 and your Apple Watch Series 3 or later to watchOS 7.4, you can enable the Unlock with Apple Watch setting. From then on, if your mask prevents Face ID from unlocking your iPhone, iOS will check to see if your watch is nearby, on your wrist, protected by a passcode, and unlocked. If so, your iPhone unlocks immediately, just as though it had scanned your face successfully. Your Apple Watch also taps your wrist to alert you and give you the option of locking the iPhone again, just in case someone has surreptitiously snagged your iPhone and is using the feature to unlock it in your presence.